2025-04-15
Ensuring Precision in Alloy Steel Casting Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide
Ensuring Precision in Alloy Steel Casting Manufacturing
Introduction to Alloy Steel Casting
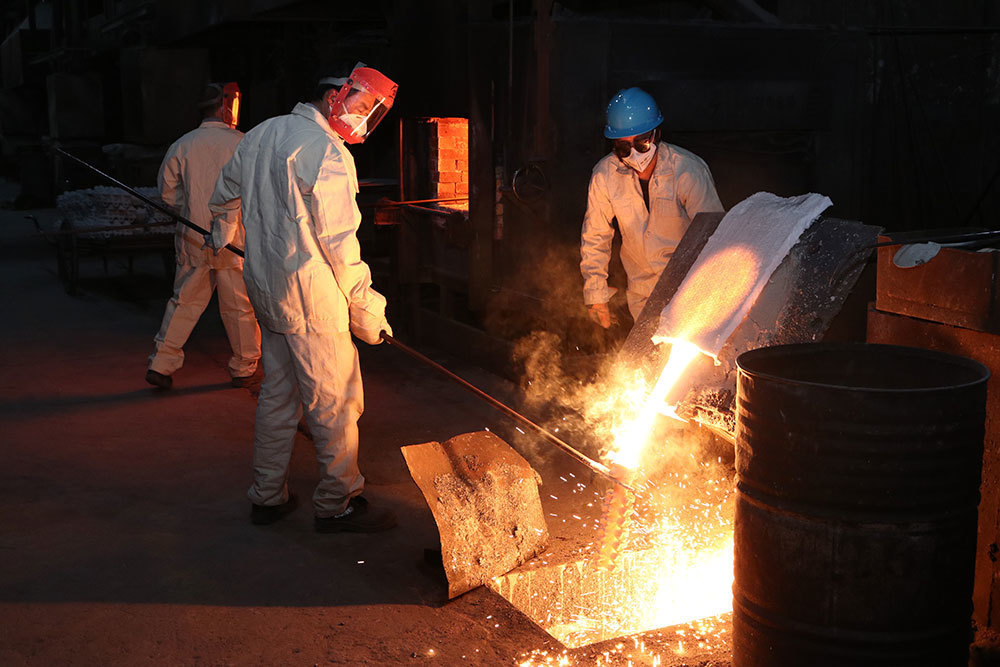
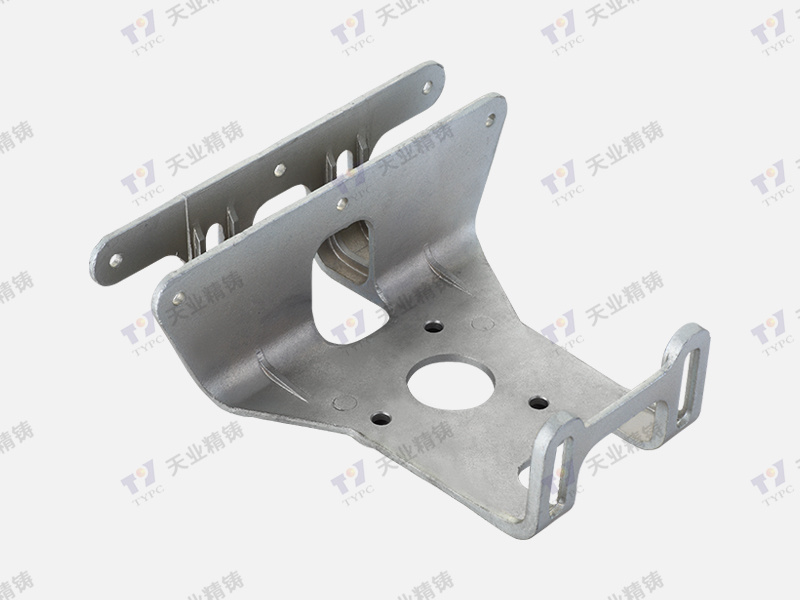
Alloy steel casting is a vital process in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. It involves pouring molten metal into molds to create complex shapes and components. Precision in this manufacturing method is crucial, as it affects the strength, durability, and performance of the final product. In this guide, we will delve into the various aspects of alloy steel casting manufacturing and explore how to ensure the highest level of precision.
The Importance of Precision in Alloy Steel Casting
Precision in alloy steel casting cannot be overstated. With applications that often operate under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or heavy loads, any deviation in the casting process can lead to catastrophic failures. Here are a few reasons why precision is paramount:
1. Enhancing Product Quality
High-precision components lead to better overall product quality. In industries like aerospace, even the slightest imperfections can compromise safety and performance. Manufacturers must prioritize precision to meet stringent quality standards.
2. Reducing Material Waste
Accurate casting processes minimize material waste, which not only reduces costs but also promotes sustainability. Efficient use of raw materials is essential in today’s environmentally conscious market.
3. Competitive Advantage
Companies that excel in precision casting can offer superior products, gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace. Clients are more likely to choose suppliers known for their quality and reliability.
Key Techniques for Achieving Precision in Casting
To ensure precision in alloy steel casting, manufacturers employ various techniques throughout the process. Each stage requires meticulous attention to detail and adherence to best practices.
1. Material Selection
The first step in precision casting is selecting the right alloy. Different alloys have unique properties, such as tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Understanding the specific requirements of the final application is crucial to choosing the appropriate material.
2. Mold Design and Fabrication
The design and fabrication of molds significantly impact the precision of cast components. Using advanced CAD software allows for the creation of highly detailed and accurate molds. Furthermore, selecting the right mold materials, such as sand or metal, can influence the casting's final dimensions.
3. Temperature Control
Maintaining the correct temperature during the melting and pouring processes is essential for achieving precision. Inconsistent temperatures can lead to defects such as shrinkage or warping. Implementing temperature monitoring systems can help ensure that the alloy is at the optimal temperature throughout the casting process.
Temperature Monitoring Techniques
Utilizing infrared thermometers and thermocouples can provide accurate temperature readings, allowing for real-time adjustments during production.
4. Pouring Techniques
The method used to pour the molten alloy into the mold plays a vital role in achieving precision. Techniques such as bottom pouring or vacuum pouring can reduce turbulence and prevent gas entrapment, ensuring a smoother flow and better filling of the mold cavity.
Challenges in Alloy Steel Casting Manufacturing
Despite advancements in technology and techniques, many challenges still arise in achieving precision in alloy steel casting.
1. Defects in Casting
Common defects, such as porosity, inclusions, and surface roughness, can compromise the integrity of the final product. Identifying the root causes of these defects is essential for implementing corrective measures.
Identifying Common Defects
- **Porosity**: Caused by trapped gas during the solidification process.
- **Inclusions**: Foreign materials that become trapped in the alloy.
- **Surface Roughness**: Typically results from poor mold design or inadequate finishing processes.
2. Variability in Raw Materials
The quality and consistency of raw materials can vary significantly, affecting the casting process. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and conducting rigorous quality checks can help mitigate these issues.
3. Maintaining Equipment and Technology
A well-maintained production line with the latest technology is crucial for precision manufacturing. Regular maintenance schedules and investing in state-of-the-art equipment can prevent breakdowns and ensure consistent quality.
Best Practices for Quality Control in Alloy Steel Casting
Implementing thorough quality control measures throughout the casting process is essential for ensuring precision.
1. In-Process Inspection
Conducting regular inspections during the casting process can help catch defects early. This proactive approach allows for timely adjustments and corrections, preventing larger issues down the line.
2. Final Product Testing
After the casting is completed, rigorous testing is essential to verify the precision of the final product. Techniques such as non-destructive testing (NDT) can identify hidden defects without compromising the component's integrity.
Common Testing Methods
- **Ultrasonic Testing**: Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws.
- **X-ray Inspection**: Reveals internal structures and potential defects through radiation.
3. Continuous Improvement Strategies
Adopting a culture of continuous improvement encourages innovation and enhances precision in the casting process. Techniques such as Six Sigma and Total Quality Management (TQM) can drive efficiency and quality.
Future Trends in Alloy Steel Casting Manufacturing
The landscape of alloy steel casting manufacturing is continually evolving. Staying ahead of trends can enhance precision and efficiency.
1. Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics in the casting process is on the rise. Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks with high precision, reducing human error and increasing production speed.
2. Advanced Materials
Research into new alloy compositions and treatments is ongoing. These advancements can improve the performance and durability of cast components, further enhancing precision.
3. Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology allows manufacturers to create a virtual representation of the casting process. This innovative tool can simulate different scenarios, helping to identify potential issues before they occur.
FAQs about Precision in Alloy Steel Casting Manufacturing
1. What are the main advantages of alloy steel casting?
Alloy steel casting offers superior strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
2. How do I choose the right alloy for my casting project?
Consider the specific application requirements, including strength, weight, and environmental factors. Consulting with material experts can also help make informed decisions.
3. What common defects should I look for during quality control?
Focus on identifying porosity, inclusions, and surface roughness during the inspection process.
4. How can temperature fluctuations affect casting quality?
Inconsistent temperatures can lead to defects such as shrinkage and warping, compromising the integrity of the casting.
5. What role does automation play in improving casting precision?
Automation enhances precision by reducing human error, increasing consistency, and speeding up production processes.
Conclusion
In the world of alloy steel casting manufacturing, ensuring precision is essential for producing high-quality components that meet rigorous industry standards. By adopting best practices, utilizing advanced techniques, and addressing common challenges, manufacturers can enhance their production processes and achieve exceptional results. As technology continues to advance, staying informed about new trends and innovations will further aid in maintaining precision and competitiveness in the market.