2025-05-05
Enhancing Wear Resistance: The Role of Alloy Steel Castings in Industrial Applications
Enhancing Wear Resistance: The Role of Alloy Steel Castings in Industrial Applications
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding Alloy Steel Castings
- 2. Benefits of Alloy Steel Castings for Wear Resistance
- 3. Types of Alloy Steel Castings
- 4. Manufacturing Process of Alloy Steel Castings
- 5. Applications of Alloy Steel Castings in Industry
- 6. Maintenance of Alloy Steel Castings
- 7. Future Trends in Alloy Steel Castings
- 8. Frequently Asked Questions
- 9. Conclusion
1. Understanding Alloy Steel Castings
Alloy steel castings are crucial components widely used in various industrial applications due to their exceptional properties. These castings are produced by introducing alloying elements into a base steel, enhancing its mechanical properties, including wear resistance, toughness, and corrosion resistance. The primary alloying elements typically include chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium, which significantly improve the material's performance in demanding environments.
The unique composition of alloy steels allows them to withstand extreme conditions, making them ideal for components subjected to high wear and tear. By understanding the fundamentals of alloy steel castings, industries can make informed decisions about their applications and benefits.
2. Benefits of Alloy Steel Castings for Wear Resistance
The advantages of alloy steel castings are numerous, particularly when it comes to wear resistance. Below are some of the key benefits:
Enhanced Durability
Alloy steel castings exhibit superior durability compared to traditional cast iron or carbon steels. The enhanced hardness achieved through controlled alloying results in a longer lifespan for components exposed to abrasive conditions, reducing the frequency of replacements and downtime in operations.
Improved Impact Resistance
The presence of alloying elements like nickel and chromium provides improved impact resistance, enabling these castings to withstand sudden shocks and stresses. This characteristic is vital for components in heavy machinery, where unexpected forces can lead to catastrophic failures.
Corrosion Resistance
Certain alloy steels are designed to resist corrosion, thus extending the lifespan of castings used in environments prone to rust and degradation. This resistance is particularly beneficial in industries such as oil and gas, where components are often exposed to harsh chemicals and moisture.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in alloy steel castings may be higher than that of standard materials, the long-term savings associated with reduced maintenance and extended service life make them a cost-effective choice. Over time, companies can save significant amounts on replacement parts and downtime.
3. Types of Alloy Steel Castings
Alloy steel castings come in various forms, each tailored for specific applications. Understanding the different types can help industries select the best option for their needs.
Low Alloy Steels
Low alloy steels typically contain less than 5% alloying elements. These castings are renowned for their excellent mechanical properties and are commonly utilized in applications requiring good strength and toughness.
Medium Alloy Steels
Medium alloy steels, containing 5% to 10% alloying elements, offer higher hardness and wear resistance compared to low alloy steels. These castings are frequently used in heavy machinery components that operate under challenging conditions.
High Alloy Steels
High alloy steels consist of more than 10% alloying elements, providing exceptional properties such as high wear resistance and corrosion resistance. These castings are ideal for specialized applications, including mining and heavy industrial equipment.
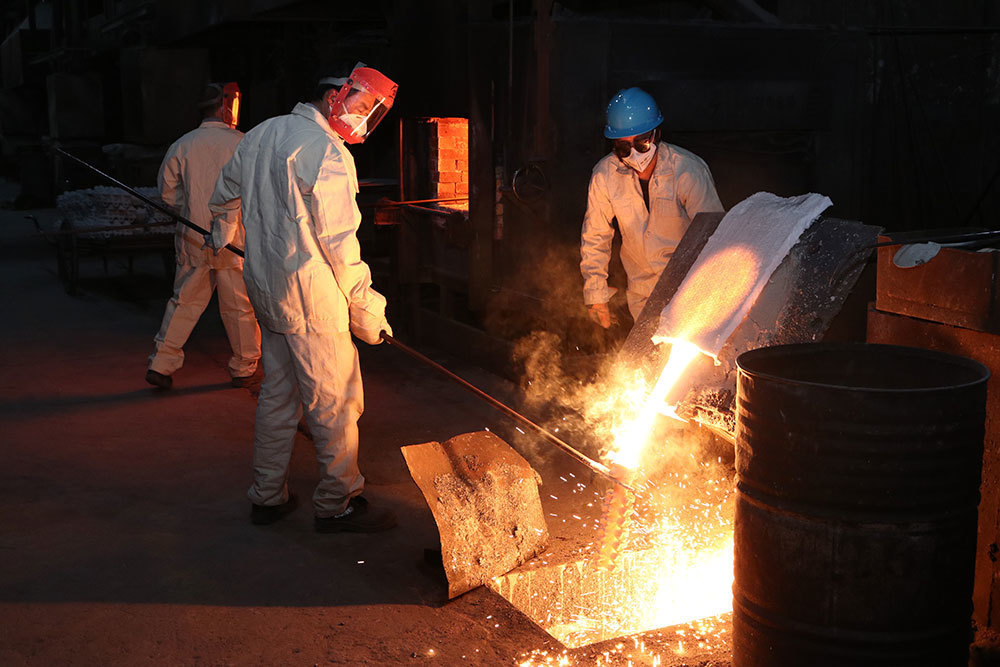
4. Manufacturing Process of Alloy Steel Castings
The manufacturing process of alloy steel castings involves several critical steps to ensure quality and performance.
Melting and Alloying
The process begins with melting the base metal and alloying elements in a crucible or electric arc furnace. The precise temperature and time are monitored to ensure complete dissolution of the alloying elements.
Pouring and Solidification
Once melted, the alloyed liquid metal is poured into molds. The cooling process must be carefully controlled to avoid defects like cracking or warping. Solidification occurs as the metal cools, taking the shape of the mold.
Heat Treatment
After solidification, heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering may be applied to further enhance the mechanical properties of the castings. These treatments can significantly improve hardness and resistance to wear.
Finishing Processes
Final finishing processes, including machining, grinding, and surface treatment, are performed to achieve the desired dimensions and surface quality. This step is crucial for ensuring that the castings meet specific tolerances required for their applications.
5. Applications of Alloy Steel Castings in Industry
Alloy steel castings find applications across various industries due to their remarkable properties. Some common applications include:
Mining Equipment
In the mining industry, components such as crusher housings, conveyor systems, and grinding mills utilize alloy steel castings to withstand harsh conditions and abrasive materials.
Agricultural Machinery
Alloy steel castings are widely used in agricultural equipment like plows and harrows, where durability and resistance to wear are essential for efficient operation.
Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas sector, alloy steel castings are crucial for valves, pumps, and other equipment that must endure high pressure and corrosive environments.
Construction Machinery
Heavy construction machinery relies on alloy steel castings for components that undergo rigorous use, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes.
6. Maintenance of Alloy Steel Castings
Proper maintenance of alloy steel castings is vital to maximize their lifespan and performance.
Regular Inspections
Routine inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of wear or damage. Early detection of issues can prevent costly failures and extend the service life of components.
Cleaning and Lubrication
Keeping alloy steel castings clean and properly lubricated can help reduce friction and wear. Implementing a regular cleaning schedule ensures that contaminants do not compromise the integrity of the materials.
Timely Repairs
If any defects are identified during inspections, timely repairs should be performed to prevent further damage. This proactive approach can save resources and ensure the continued efficiency of machinery.
7. Future Trends in Alloy Steel Castings
The future of alloy steel castings is promising, with several trends shaping the industry:
Advancements in Alloying Techniques
Developments in alloying technology are leading to the creation of new steel compositions that offer even better wear resistance and performance. Research in nanostructured materials is paving the way for high-performance alloys.
Sustainability Practices
The focus on sustainability is leading to the use of recycled materials in the production of alloy steel castings. This trend not only conserves resources but also minimizes environmental impact.
Smart Manufacturing
The integration of IoT and smart technologies in the manufacturing process is enhancing quality control and efficiency. These innovations are expected to streamline production and ensure consistent quality in alloy steel castings.
8. Frequently Asked Questions
What are alloy steel castings made of?
Alloy steel castings are made from a combination of steel and various alloying elements, such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, and vanadium, which enhance their mechanical properties.
How do alloy steel castings improve wear resistance?
The alloying elements in steel increase hardness and toughness, allowing the material to withstand wearing conditions without significant degradation.
What industries commonly use alloy steel castings?
Alloy steel castings are used across various industries, including mining, agriculture, oil and gas, and construction, due to their durability and resistance to wear.
How can I maintain alloy steel castings?
Regular inspections, cleaning, lubrication, and timely repairs are essential for maintaining alloy steel castings and extending their lifespan.
What is the difference between low, medium, and high alloy steels?
Low alloy steels contain less than 5% alloying elements, medium alloy steels have 5% to 10%, and high alloy steels consist of over 10%, resulting in varying levels of hardness and wear resistance.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, alloy steel castings are pivotal in improving wear resistance across various industrial applications. Their unique properties, derived from the appropriate combination of alloying elements, enable them to withstand harsh environments and demanding operational conditions. As industries continue to evolve, so will the advancements in alloy steel technology, leading to enhanced performance and sustainability. By understanding the benefits, types, and maintenance of alloy steel castings, industries can optimize their applications, ensuring efficient and durable machinery for years to come.