2025-05-06
Understanding Heat Resistant Steel Casting: A Key Component in Industrial Applications
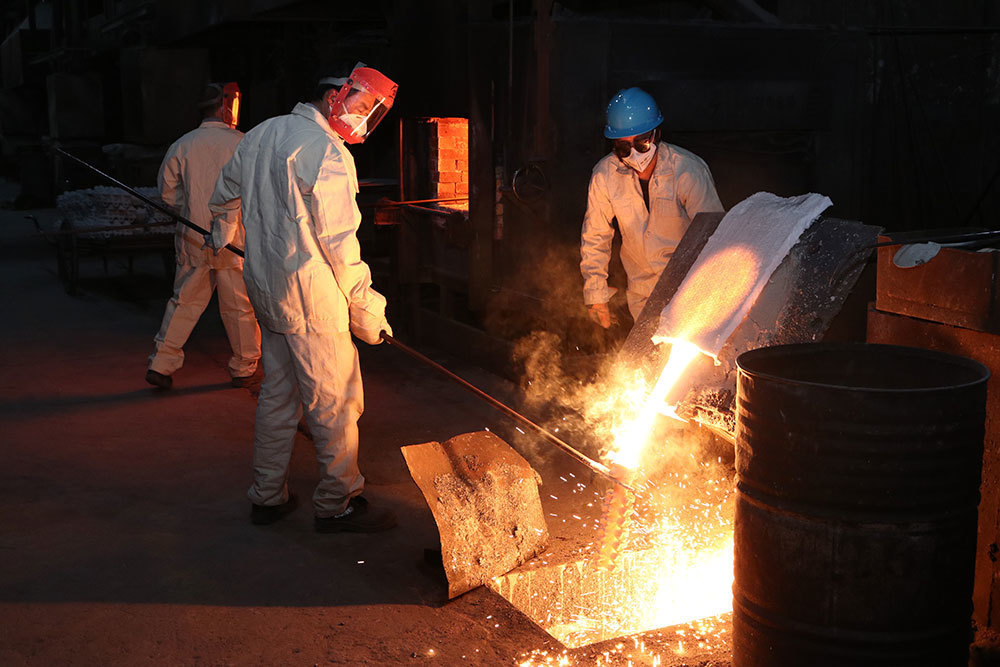
Heat resistant steel casting is a crucial material in the industrial equipment and component sector, particularly in applications where temperatures can soar. This type of steel is engineered to withstand high thermal stress, making it an excellent choice for various industrial applications, including manufacturing components that are exposed to extreme heat.
One of the primary characteristics of heat resistant steel casting is its ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures. Unlike regular steel, which can lose strength and become malleable when heated, heat resistant steel retains its hardness and toughness. This is achieved through specific alloying elements that are added during the casting process. Common alloying elements include chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, which enhance the steel’s resistance to oxidation and thermal fatigue.
The manufacturing process of heat resistant steel casting typically involves precision techniques such as sand casting or investment casting. These methods allow for complex shapes and sizes to be produced with a high degree of accuracy. In addition, the casting process can be tailored to meet specific requirements, such as dimensional tolerances and surface finishes, which can be critical in ensuring the functional performance of the final product.
Heat resistant steel castings are used in various applications, including heat exchangers, furnace components, and turbine parts. For instance, in the aerospace industry, components made from heat resistant steel must withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining performance and safety standards. Similarly, in power generation, turbines rely on these materials to function efficiently without succumbing to thermal degradation.
Another significant advantage of heat resistant steel casting is its longevity. Components made from this material often exhibit extended service life due to their resistance to thermal cycles and corrosion. This longevity translates into reduced downtime and maintenance costs, making heat resistant steel castings an economical choice in the long run.
When selecting heat resistant steel castings for your applications, it’s essential to consider factors such as the specific temperature range, exposure to corrosive environments, and mechanical load requirements. Working with material experts can help you understand the various grades of heat resistant steels available and determine the best fit for your particular needs.
In summary, heat resistant steel casting plays an essential role in the manufacturing of robust industrial components capable of withstanding high temperatures. Its unique properties, processing techniques, and applicable uses make it a preferred choice for industries that demand reliability and performance under extreme conditions. By understanding the benefits and characteristics of heat resistant steel casting, manufacturers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
One of the primary characteristics of heat resistant steel casting is its ability to maintain structural integrity at elevated temperatures. Unlike regular steel, which can lose strength and become malleable when heated, heat resistant steel retains its hardness and toughness. This is achieved through specific alloying elements that are added during the casting process. Common alloying elements include chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, which enhance the steel’s resistance to oxidation and thermal fatigue.
The manufacturing process of heat resistant steel casting typically involves precision techniques such as sand casting or investment casting. These methods allow for complex shapes and sizes to be produced with a high degree of accuracy. In addition, the casting process can be tailored to meet specific requirements, such as dimensional tolerances and surface finishes, which can be critical in ensuring the functional performance of the final product.
Heat resistant steel castings are used in various applications, including heat exchangers, furnace components, and turbine parts. For instance, in the aerospace industry, components made from heat resistant steel must withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining performance and safety standards. Similarly, in power generation, turbines rely on these materials to function efficiently without succumbing to thermal degradation.
Another significant advantage of heat resistant steel casting is its longevity. Components made from this material often exhibit extended service life due to their resistance to thermal cycles and corrosion. This longevity translates into reduced downtime and maintenance costs, making heat resistant steel castings an economical choice in the long run.
When selecting heat resistant steel castings for your applications, it’s essential to consider factors such as the specific temperature range, exposure to corrosive environments, and mechanical load requirements. Working with material experts can help you understand the various grades of heat resistant steels available and determine the best fit for your particular needs.
In summary, heat resistant steel casting plays an essential role in the manufacturing of robust industrial components capable of withstanding high temperatures. Its unique properties, processing techniques, and applicable uses make it a preferred choice for industries that demand reliability and performance under extreme conditions. By understanding the benefits and characteristics of heat resistant steel casting, manufacturers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.