2025-05-26
Understanding Heat Resistant Steel Casting: Key Insights for Industrial Applications
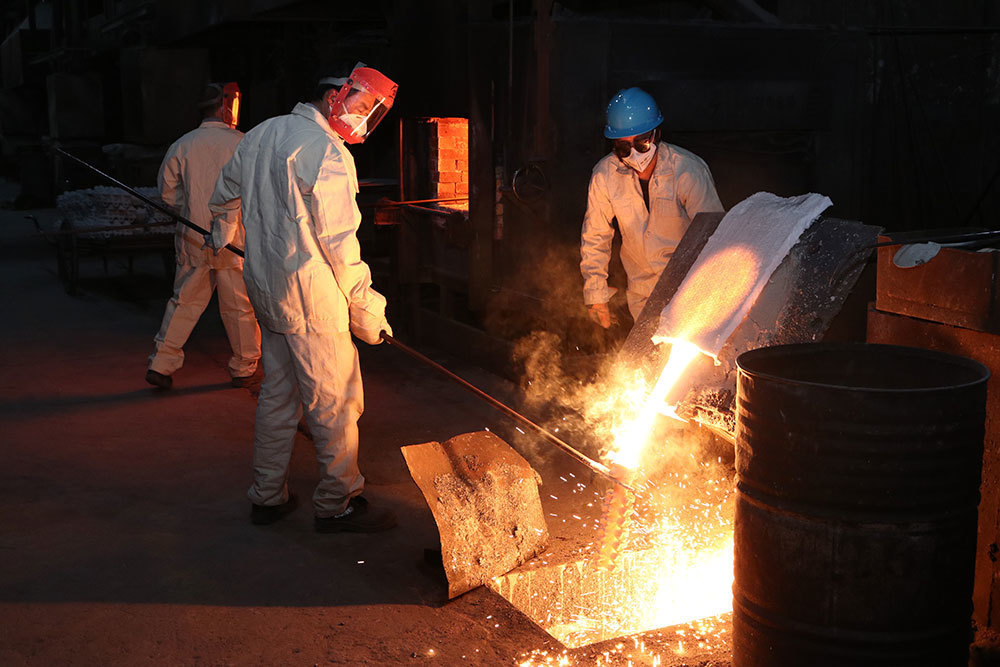
Heat resistant steel casting is a specialized process used to create components that can withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining structural integrity. This type of casting is essential in industries where high thermal stress is common, such as in power generation, aerospace, and heavy machinery. Understanding the properties and applications of heat resistant steel casting can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of industrial components.
One of the primary characteristics of heat resistant steel is its ability to maintain strength and toughness at elevated temperatures. This quality is largely attributed to the alloying elements present in the steel, such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. These elements work together to form a protective oxide layer on the surface of the steel, which helps to resist oxidation and corrosion. Additionally, heat resistant steel casting often incorporates other elements to further enhance performance, such as vanadium, which can improve high-temperature strength.
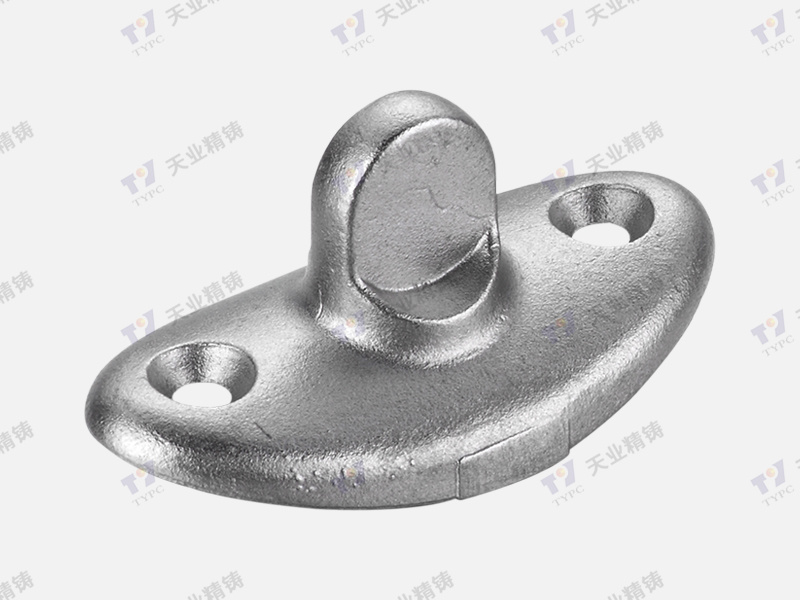
In practical applications, heat resistant steel castings are commonly utilized for components such as furnace linings, exhaust systems, and turbine blades. The durability of these castings ensures that they can withstand not only high temperatures but also the mechanical stresses associated with operation in harsh environments. For example, in power plants, components made from heat resistant steel casting are critical for maintaining efficiency and operational safety.
Another significant advantage of heat resistant steel casting is its versatility. Depending on the specific requirements of the application, different grades of heat resistant steel can be selected to optimize performance. This flexibility allows manufacturers to tailor their components for specific operational conditions, resulting in reduced wear and longer service life.
From a manufacturing perspective, heat resistant steel casting can be complex, requiring precise control over the casting process. Careful attention must be paid to factors such as melting temperature, cooling rates, and mold materials to ensure the desired mechanical properties are achieved. Advanced casting techniques, such as investment casting and sand casting, are often employed to produce intricate shapes and designs that meet industry standards.
In conclusion, understanding heat resistant steel casting is vital for professionals in the industrial sector. Its ability to perform under extreme conditions makes it indispensable for various applications. By leveraging the unique properties of heat resistant steel, manufacturers can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their equipment, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for advanced materials like heat resistant steel casting is expected to grow, making it an important area of focus for engineers and manufacturers alike.
One of the primary characteristics of heat resistant steel is its ability to maintain strength and toughness at elevated temperatures. This quality is largely attributed to the alloying elements present in the steel, such as chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. These elements work together to form a protective oxide layer on the surface of the steel, which helps to resist oxidation and corrosion. Additionally, heat resistant steel casting often incorporates other elements to further enhance performance, such as vanadium, which can improve high-temperature strength.
In practical applications, heat resistant steel castings are commonly utilized for components such as furnace linings, exhaust systems, and turbine blades. The durability of these castings ensures that they can withstand not only high temperatures but also the mechanical stresses associated with operation in harsh environments. For example, in power plants, components made from heat resistant steel casting are critical for maintaining efficiency and operational safety.
Another significant advantage of heat resistant steel casting is its versatility. Depending on the specific requirements of the application, different grades of heat resistant steel can be selected to optimize performance. This flexibility allows manufacturers to tailor their components for specific operational conditions, resulting in reduced wear and longer service life.
From a manufacturing perspective, heat resistant steel casting can be complex, requiring precise control over the casting process. Careful attention must be paid to factors such as melting temperature, cooling rates, and mold materials to ensure the desired mechanical properties are achieved. Advanced casting techniques, such as investment casting and sand casting, are often employed to produce intricate shapes and designs that meet industry standards.
In conclusion, understanding heat resistant steel casting is vital for professionals in the industrial sector. Its ability to perform under extreme conditions makes it indispensable for various applications. By leveraging the unique properties of heat resistant steel, manufacturers can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their equipment, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for advanced materials like heat resistant steel casting is expected to grow, making it an important area of focus for engineers and manufacturers alike.