2025-06-08
Unlocking the Potential of Stainless Steel Casting Technologies
Unlocking the Potential of Stainless Steel Casting Technologies
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Stainless Steel Casting
2. Understanding Stainless Steel: Composition and Properties
3. The Process of Stainless Steel Casting
3.1. Different Casting Methods Explained
3.2. Advantages of Using Stainless Steel in Casting
4. Applications of Stainless Steel Casting Technologies
4.1. Industrial Machinery and Equipment
4.2. Automotive Components
4.3. Aerospace Applications
5. Emerging Trends and Innovations in Stainless Steel Casting
6. Sustainability and Stainless Steel Casting
7. Challenges in Stainless Steel Casting Technologies
8. Future Prospects of Stainless Steel Casting
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10. Conclusion
1. Introduction to Stainless Steel Casting
Stainless steel casting is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape by providing durable and reliable components for various industries. This process combines the advantages of stainless steel with advanced casting techniques to produce high-quality parts that withstand extreme conditions. As industries evolve and demand for specialized components increases, understanding the potential of stainless steel casting becomes crucial for manufacturers seeking competitive advantages.
2. Understanding Stainless Steel: Composition and Properties
Stainless steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron, carbon, and chromium, which imparts corrosion resistance and enhances durability. The addition of other elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and manganese further improves its mechanical properties. This unique composition results in a material that is not only strong but also resistant to oxidation, making it ideal for a variety of applications.
The **properties** of stainless steel, such as high tensile strength, resistance to thermal expansion, and excellent weldability, make it a preferred choice for casting. Manufacturers leverage these properties to create components that require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan.
3. The Process of Stainless Steel Casting
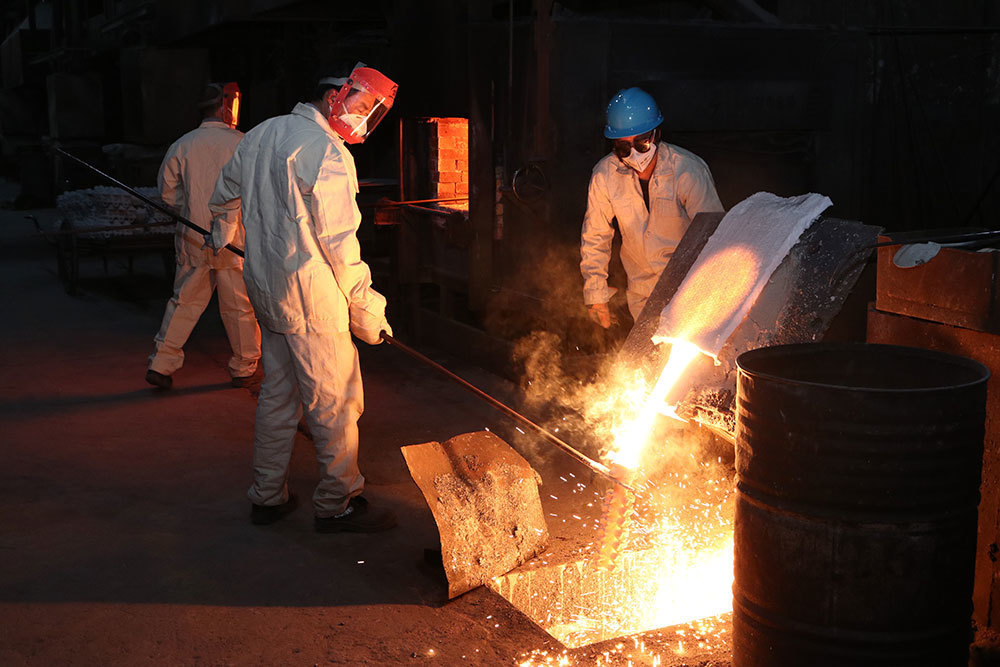
Casting stainless steel involves several processes that transform raw materials into finished products. Understanding these processes is key to unlocking the full potential of stainless steel casting technologies.
3.1. Different Casting Methods Explained
There are several methods of stainless steel casting, each suited for specific applications:
- **Investment Casting**: This method, also known as precision casting, involves creating a wax pattern coated with a ceramic shell. Once the shell is hardened, the wax is melted away, and molten stainless steel is poured in. This technique offers high precision and is ideal for complex shapes.
- **Sand Casting**: In this traditional method, sand is used to create molds. While it may not provide the same level of detail as investment casting, it is cost-effective and suitable for large components.
- **Die Casting**: Involves forcing molten stainless steel into molds under high pressure. This method is efficient for mass production and results in smooth surface finishes.
- **Centrifugal Casting**: Used for cylindrical parts, this technique utilizes centrifugal force to distribute molten metal evenly within the mold, ensuring uniform density.
3.2. Advantages of Using Stainless Steel in Casting
The advantages of stainless steel in casting are numerous:
- **Corrosion Resistance**: Stainless steel's inherent resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for harsh environments.
- **Durability**: Components made from stainless steel have a longer lifespan compared to those made from other materials.
- **Versatility**: Its ability to be molded into complex shapes allows for a wide range of applications.
- **Aesthetic Appeal**: Stainless steel has a modern appearance, making it suitable for architectural and decorative applications.
4. Applications of Stainless Steel Casting Technologies
Stainless steel casting technologies serve diverse industries, enhancing performance and reliability in various applications.
4.1. Industrial Machinery and Equipment
In industrial settings, stainless steel castings are crucial for machinery components, including pumps, valves, and fittings. Their resistance to wear and corrosion ensures efficient operation and reduced downtime.
4.2. Automotive Components
The automotive industry relies on stainless steel castings for parts that require strength and durability, such as exhaust systems, engine blocks, and chassis components. The ability to produce lightweight yet strong parts contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
4.3. Aerospace Applications
In aerospace, where safety and reliability are paramount, stainless steel castings are used for critical components such as landing gear and turbine housings. The rigorous testing and standards ensure that these components can withstand extreme conditions.
5. Emerging Trends and Innovations in Stainless Steel Casting
As technology advances, new trends are shaping the future of stainless steel casting. Innovations such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) are enabling manufacturers to produce more complex and customized components. Furthermore, advancements in alloy formulations are enhancing the performance characteristics of stainless steel, allowing for even more applications.
6. Sustainability and Stainless Steel Casting
Sustainability is a growing concern in manufacturing, and stainless steel casting technologies are addressing this issue. The recycling potential of stainless steel is one of its most significant advantages. It can be recycled without losing its properties, contributing to a circular economy. Manufacturers are also adopting eco-friendly production methods and reducing waste throughout the casting process.
7. Challenges in Stainless Steel Casting Technologies
Despite its advantages, stainless steel casting presents challenges. The high cost of raw materials and the complexity of the casting processes can pose obstacles for manufacturers. Additionally, achieving the desired mechanical properties and surface finishes requires precise control over the casting process.
8. Future Prospects of Stainless Steel Casting
The future of stainless steel casting looks promising. With continuous advancements in technology and materials, the potential applications are expanding. Industries are increasingly turning to stainless steel casting to meet their demanding requirements, and manufacturers who invest in these technologies will likely gain a competitive edge in the market.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the main advantages of stainless steel casting?
A1: The primary advantages include corrosion resistance, durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal.
Q2: What industries benefit the most from stainless steel casting technologies?
A2: Major industries include automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, and construction.
Q3: How does stainless steel casting compare to other casting materials?
A3: Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and mechanical properties compared to materials like aluminum or iron.